When you go to your doctor for an examination and are referred for a scan, you might wonder what a CT scan or an MRI actually are. Both of these tests are used to check for abnormalities in the body. They can help detect tumours, locate sources of pain, and reveal other helpful information about your health.
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are two types of medical imaging procedures used to diagnose diseases and monitor the progress of treatment or prevention programs. Both use very different techniques to achieve their diagnostic goals. So what are the differences between MRI scans and CT scans?
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan is a medical imaging procedure that uses X-ray technology to create a three-dimensional image of the inside of an object. The image is formed from an X-ray beam that rotates around the object being examined and passes through the object. The beam is then detected and recorded by a computer system that produces cross-sectional images.
Colloquially, "CT scan" is often a catch-all phrase to describe CT and CT angiography imaging procedures. CT angiography is a type of CT scanning done by adding a particular injection or IV dye that allows for imaging of blood vessels. This type of CT scanning is used to study the blood vessels both near the surface of the skin as well as deep within the body.
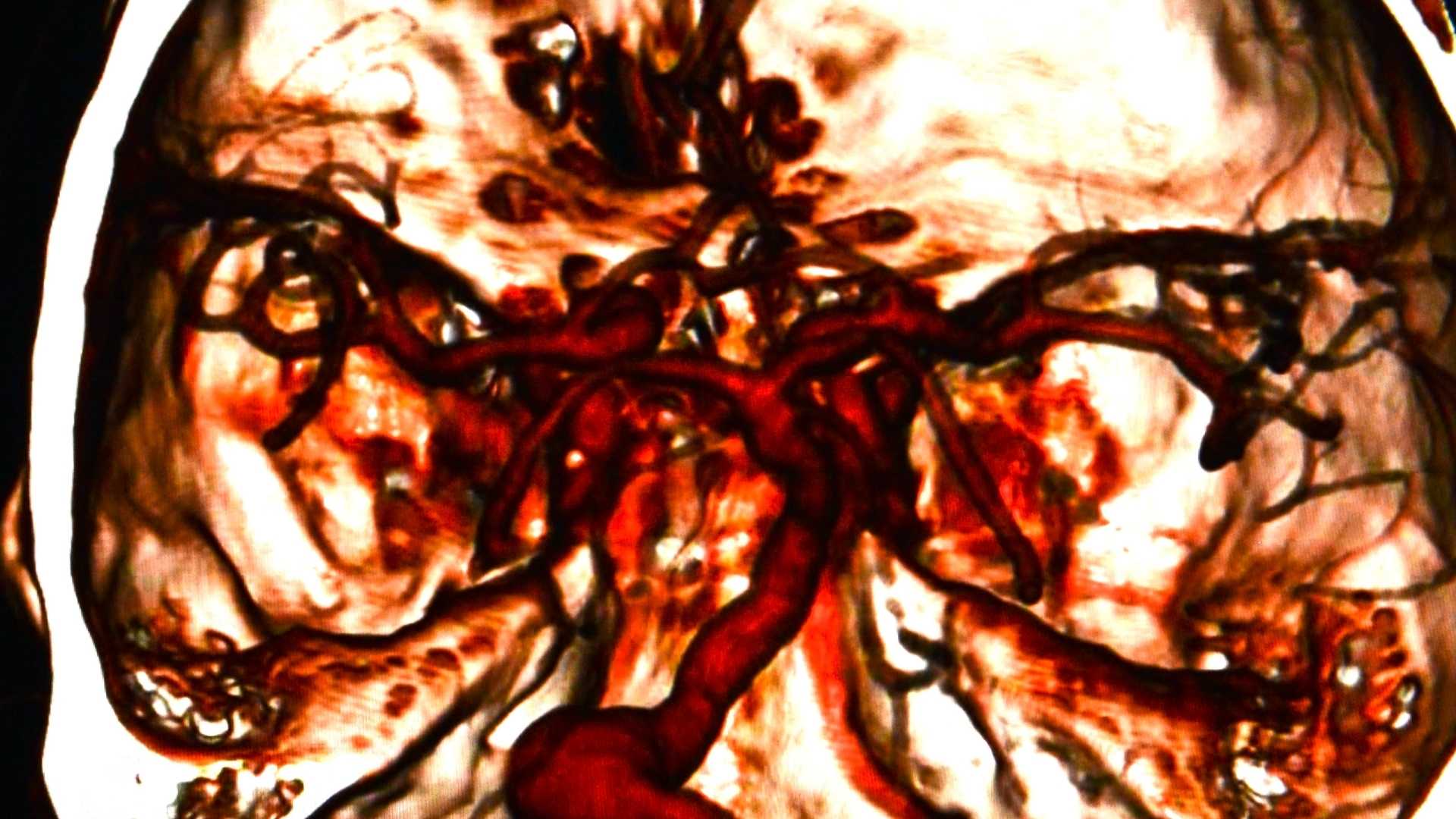
What is an MRI?
A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan is a medical imaging procedure that uses a strong magnetic field and pulses of radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of your body. To get an MRI scan, the patient lies on a table that is slid inside a large cylindrical magnet. The magnet creates a strong magnetic field to align the hydrogen atoms in water molecules throughout your body. Radio waves are then sent through the patient’s body.
The magnetic field causes the water in your body to resonate at a frequency that depends on the amount of hydrogen it contains. This resonance is then picked up by a sensor that records the information and turns it into a 3D image. These MRI scanners use a solid electromagnet to create a magnetic field, whereas CT scanners use an X-ray machine.
MRI scanners emit low levels of radiofrequency radiation (much less than you are exposed to on a daily basis going about regular activities), and none of the radiation is in the form of ionising radiation. The radiation risk associated with having an MRI is extremely low, and many people can safely have MRIs with no special precautions.
How are CT Scans and MRIs Different?
The most significant difference between MRI and CT scans is that MRI scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of your body, while CT scans use X-rays. MRI scans are more accurate than CT scans in certain situations.
In some cases, MRI scans are able to provide higher resolution images and detect abnormalities that might be missed during a CT scan.
CT scans are generally less expensive than MRIs if not covered by Medicare Bulk Billing and can provide quick results. That said, MRIs have become more widely available in recent years, and their costs have decreased, making them more affordable if you do have to pay for one.
Even if the imaging practice you have been referred to does not bulk bill, part of the cost of either type of scan can be recouped through a Medicare rebate.
Differences in Usage
CT scans are generally used to quickly generate cross-sectional images of areas inside the body that are close to the surface. This includes scans of the head, neck, abdomen, and chest. MRIs commonly produce images of the spine, joints, muscles, and internal organs.
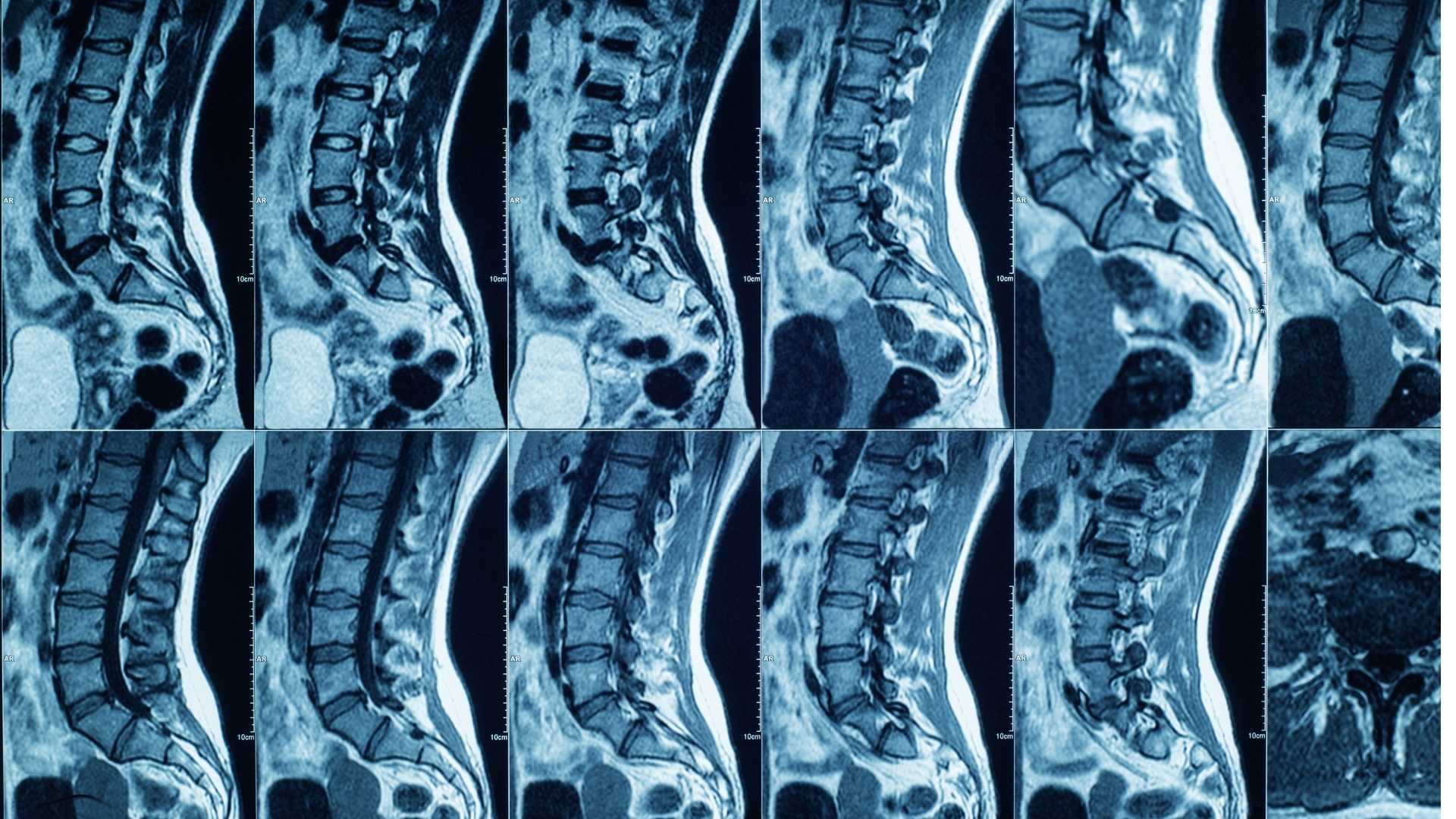
Differences in Equipment and Technology
CT scanners emit X-rays to create body images, while MRI scanners use magnetic fields and radio waves. These two technologies create different images with different levels of detail. MRI scanners are larger machines filled with a special liquid (usually a type of oil). CT scanners, on the other hand, are much smaller and can be wheeled right up to the patient being examined. MRI scanners are also generally more expensive than CT scanners.
Limitations and Risks
CT scans are often better at detecting abnormalities in soft tissue, such as tumours and cysts. MRIs, on the other hand, provide much more detailed images of the bones and internal organs. In some cases, MRI scans cannot detect abnormalities visible during a CT scan. Some types of tumours and cysts are too large to be detected through MRI scanning.
In rare cases, MRI scans can cause an allergic reaction. MRIs are generally considered to be safer than CT scans. MRI scanners emit low levels of radiofrequency and no ionising radiation, which is considered more harmful. CT scans, on the other hand, emit significantly higher levels of ionising radiation.
Although you can book a scan for yourself, typically you will be referred for a scan due to illness or injury. A referral is required for bulk billing or a Medicare rebate. If you are injured or ill, and need to seek help, don’t hesitate to book an appointment with a doctor near you.
The fastest and easiest way to search for and book healthcare appointments online is at MyHealth1st.com.au